Heat Exchangers
HEAT EXCHANGER
Through high technology engineering and high quality we manufacturing to our customers our heat exchangers to be solutions to their demand in industry
Explore our products
Products
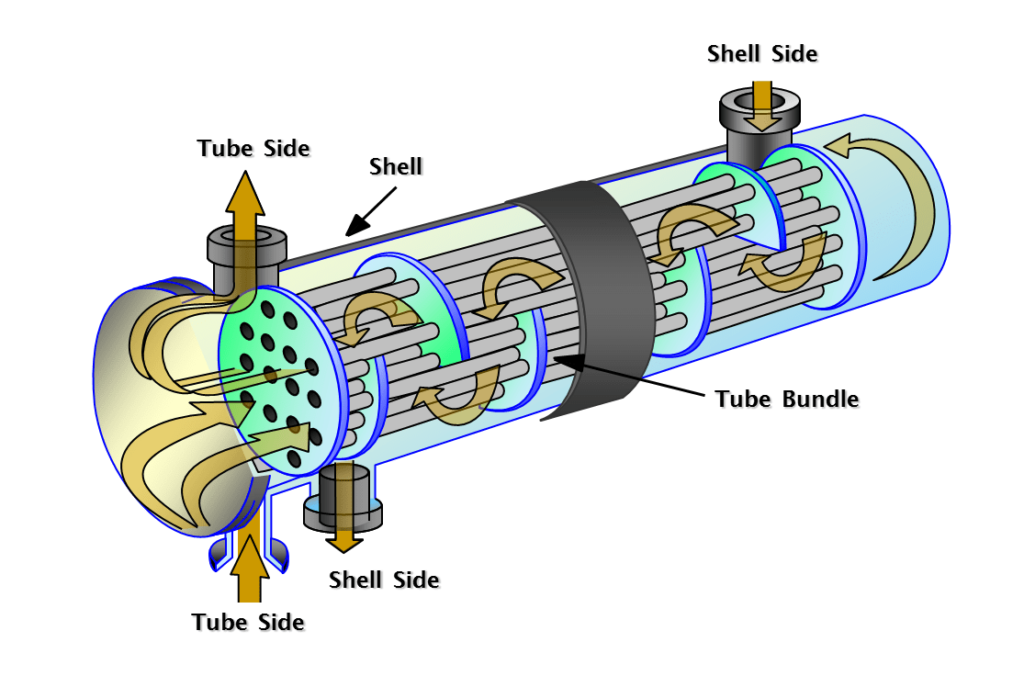
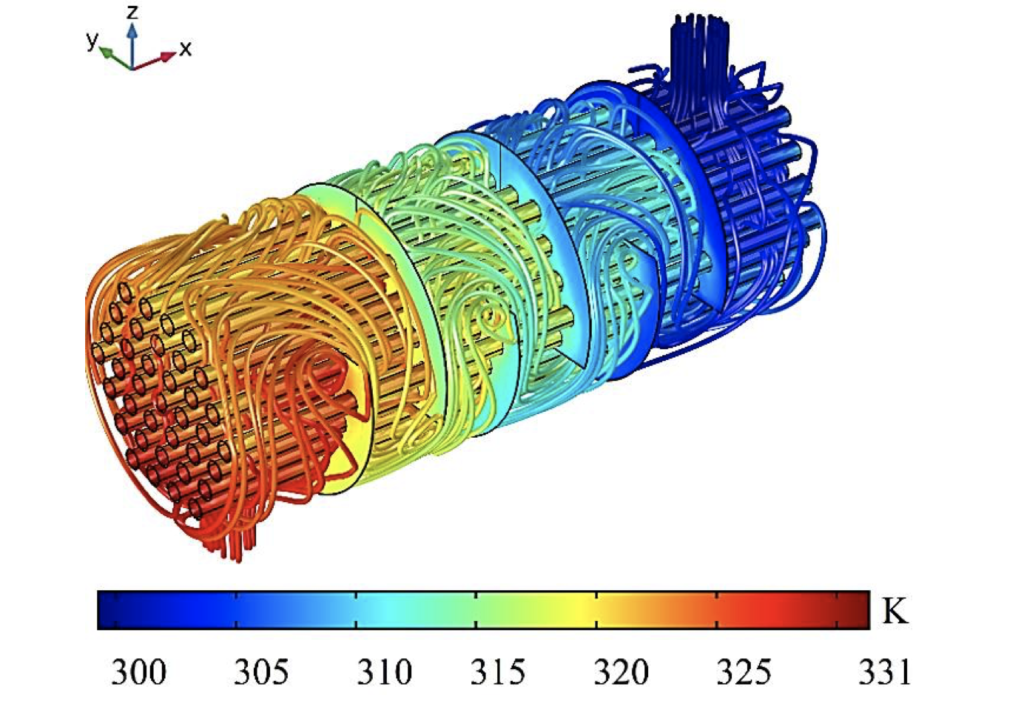
Heat exchangers are designed to transfer heat from a working fluid to a secondary fluid or the surrounding air. The heat exchanger relies on the efficient heat transfer that occurs during phase changes, in this case during the condensation of a vapor into a liquid.
Countless variations exist in heat exchanger design, with design variables including the working fluid, the secondary fluid, the geometry and the material. Common secondary fluids include water, air, refrigerants, or phase-change materials.
Heat exchanger have two significant design advantages over other cooling technologies:
Heat transfer by latent heat is much more efficient than heat transfer by sensible heat only
The temperature of the working fluid stays relatively constant during condensation, which maximizes the temperature difference between the working and secondary fluid.
There are various types of heat exchangers;
- Double tube
- Shell and tube
- Tube in tube
- Plate heat
- Scraped surface
- Finned
Benefits of Heat Exchangers in Processing Systems;
- Smaller spatial footprint
- Lower environmental impact
- Minimal operating costs
- Adaptable
- Cost and Maintenance